TD 1 - Computational geometry in Java
The objective of this first lab session is to implement some basic geometric algorithms in 2D and to become familiar with the Jcg library, as well as its data structures and geometric primitives.
0. Libraries to download
Before starting this TD session, the Jcg library must be downloaded and installed, as explained below.
- The source code of the Jcg library can be download here: Jcg.zip.
- The Javadoc of the Jcg library can be found here. Do not hesitate to take a look !
- The Processing library (version 1.51) can be download here: core.jar.
- The TC library (for input/output on text files) can be download here: TC.jar.
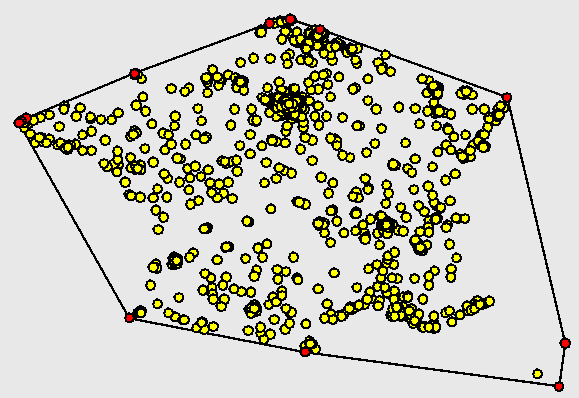
In this exercise, you are asked to implement the sweep algorithm presented in class for computing convex hulls in the plane. Once this is completed, you will also be able to implement the gift-wrapping algorithm.
Here is a solution
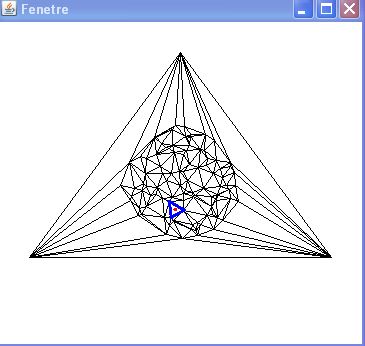
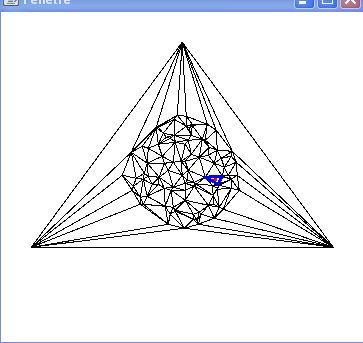
In this exercise, we will use the elementary navigation operations provided by the Half-edge structure to implement a simple point-location algorithm in a planar mesh.
Below are two examples of the execution of a point-location algorithm in a triangulation based on a random walk.
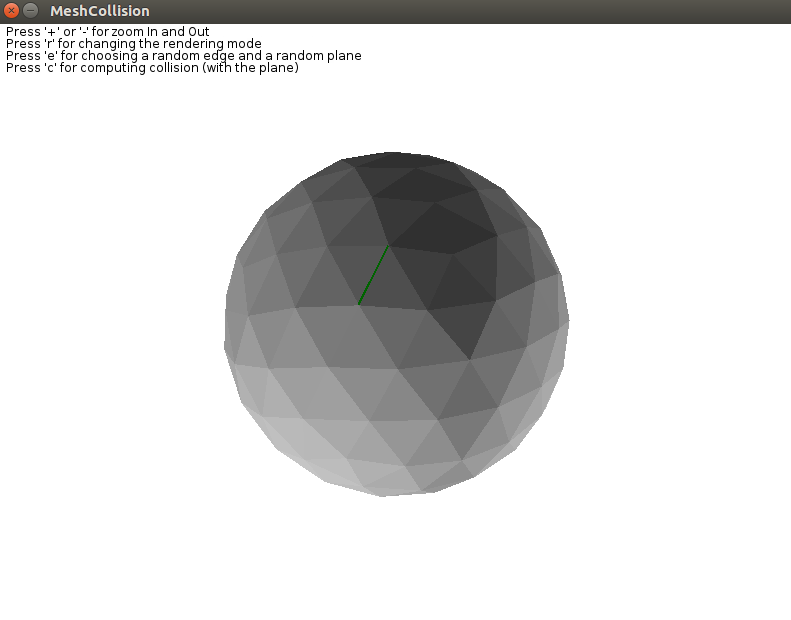
This exercise introduces a fundamental data structure in algorithmic geometry, known as the half-edge structure, which makes it possible to represent orientable combinatorial surfaces, both triangulated and polygonal. In particular, we will use the elementary navigation operations within a mesh to implement a simple algorithm for computing the set of faces of a triangular mesh that are intersected by a randomly chosen hyperplane.